With all eyes on 2050 and the mid-century point, a highly ambitious series of global programs are in place to reduce carbon emissions simultaneously aiming to upgrade all forms of transport with their green equivalent—land, air, sea. Electric power stands at the center of this revolution, and at the center of the center stands the power module. Within this particular ecosystem, two principle types dominate power modules: the metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor or MOSFET power module and the insulated-gate bipolar transistor or IGBT power module. These modules provide the physical containment for components governing the practical operation, for example, as a switching element in power converters allowing variable speed drives to stop or start or vary the power flow. This blog pays principle consideration to IGBT modules.

IGBT power-modules come in a variety of voltages, current ratings, topologies, and applications. The requirements for a carbon-free economy are, however, significantly widen market growth beyond electric vehicles to elevators, motor converters, solar energy, welding, industrial frequency converters, pumps, large scale medical devices, and many additional daily human life influencing Applications. This, in turn, is shaping packaging technologies in the direction of power density and module integration, as well as making issues of performance, efficiency, longevity, and reliability more critical than ever. All those mentioned above must be met with cost-effective, innovative solutions that are concomitantly geared to move with the dynamics—and surprises—of evolving technologies.
Fig. 1 Projected Electric Vehicle Sales Worldwide 2025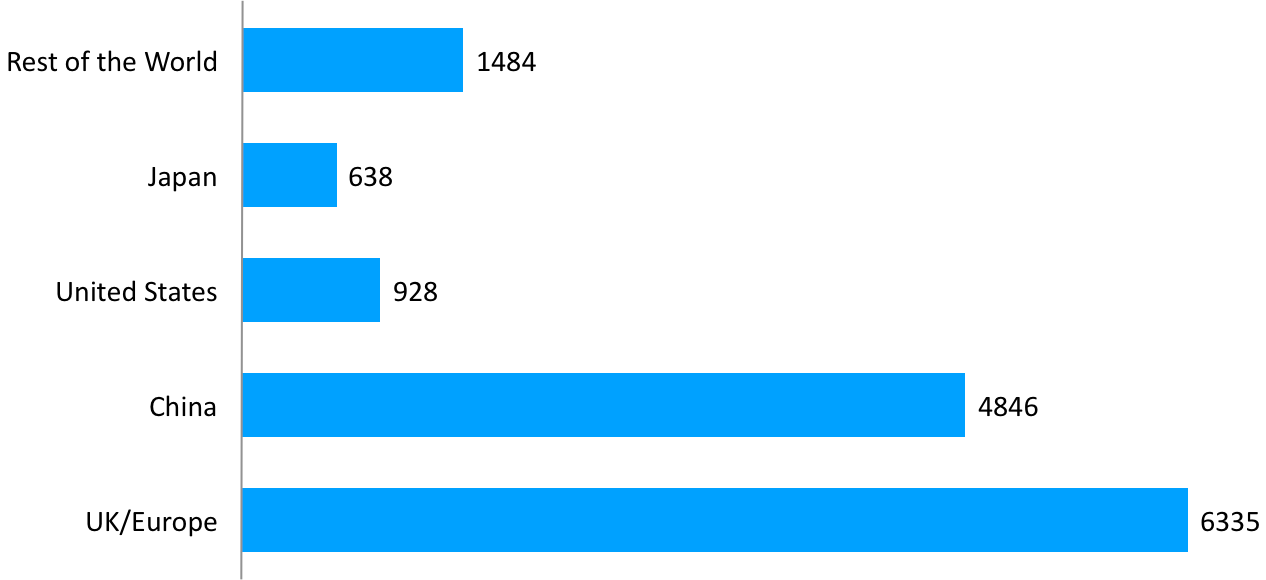
Source: Union Bank of Switzerland
In terms of growth specifics, decarbonization is by far the most significant factor behind driving future demand for power modules and the technologies they enable. The IGBT Power Module market has been forecast to grow at 9.2 percent CAGR between now and 2026 reaching an estimated value of US $9.9 billion (Fortune and Business Insights, January 2020).
This broader and sustained demand for green power must be understood as the convergence of five principal factors:
- Growing perceived dangers of climate change and increased urgency of the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions/move towards green energies.
- The particular vulnerability of China and other Asian nations to potentially catastrophic environmental consequences should global warming rise above 2°.
- Growing demand for energy from emerging economies, especially in Africa, where eco-power is seen as the easiest and most effective solution to local needs as well as the most beneficial application of development aid.
- Legislative push in Europe and Asia requiring HEV/EV only automotive sales from the 2030s. See Fig. 1 above.
- The rapid rise in demand for other forms of electric powered transport (bus, trucks, trains, etc.) from Europe and China.
- Move towards hybrid/electric power passenger flight/utility drones from 2025 onwards.
These factors are helping to drive a wide range of energy-efficient innovations, principally in the arenas of power generation (wind, wave, solar), power storage (batteries), and electric power for transport (vehicular, drone, aeronautics). While improvements to power production and power trains are essential, the most technically challenging constituent within the overall ecosystem is the traction inverter. This critical component in the electrified drive-train has a direct influence on the driving experience, the battery range, and the overall safety of the vehicle.
Turning to the industry roadmaps for module packaging, we may note the following concerning targeted improvements: commercial parameters, module footprint, thermal capacity, scalability, and reliability. In short, cost and performance remain the dominant imperatives. What may come as a surprise to some is that commercial vehicles need to be improved by an entire magnitude of order over and against domestic use; for example, 70,000 lifetime hours over and against 7000 hours. Other important packaging issues include lifespan, modular proximity/compactness, and temperature/cooling. Furthermore, the technology needs to be adaptable to span battery electric vehicles (BEV), plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV), and full hybrid vehicles (HEV). Finally, it needs to be evolving. Products need to move swiftly in the development chain to match the rapid advance in, and ever-wider adoption of, electric powertrains on land, at sea and in the air.
Land, air, and sea are only the beginning of a longer list of possible operating environments for power modules. Outer space, deep sea, nuclear facilities, battle zones, and the human body are among the future needs—and challenges facing packaging developers. From Rad exposure to pressure to extreme vibration. Where these will go and how the technologies will evolve remains uncertain, but what we do know is that with transport needs dominating the market, whatever else happens all will be constrained by the needs of cost-effective manufacturing methods and ever-rising levels of reliability.
In anticipation of these dynamics, SST Vacuum Reflow Systems, a Palomar solution, has developed the new 8300 Series Automated Vacuum Pressure Soldering System, which is modular and scalable to meet the desired UPH. The SST 8300 Series is an automated vacuum pressure soldering system designed to deliver a reliable low-void, flux-less solder process using a precise combination of vacuum and gas pressure. It has been specifically designed to provide a highly secure solder connection with less than 1% void rate – a key to delivering high-reliability power modules for automotive and commercial applications.
Vacuum Pressure Soldering System, which is modular and scalable to meet the desired UPH. The SST 8300 Series is an automated vacuum pressure soldering system designed to deliver a reliable low-void, flux-less solder process using a precise combination of vacuum and gas pressure. It has been specifically designed to provide a highly secure solder connection with less than 1% void rate – a key to delivering high-reliability power modules for automotive and commercial applications.
Additionally, the vacuum reflow process of the 8300 Series is lead-free and meets critical ecological demands. The SST 8300 Series Automated Vacuum Pressure Soldering System differs from current systems on the market by utilizing SST’s unique method of applying both vacuum and gas pressure for the soldering interface of critical components inside a power module, especially for DBC-to-base plate soldering.
Download these resources for more information:
----
Dr. Anthony O'Sullivan
Palomar Technologies
Strategic Market Research Specialist


